Follow Us
Join our newsletter
We will get back to you as soon as possible
Please try again later
By Selin Oğuz Graphics/Design: Alejandra Dander | Clayton Wadsworth
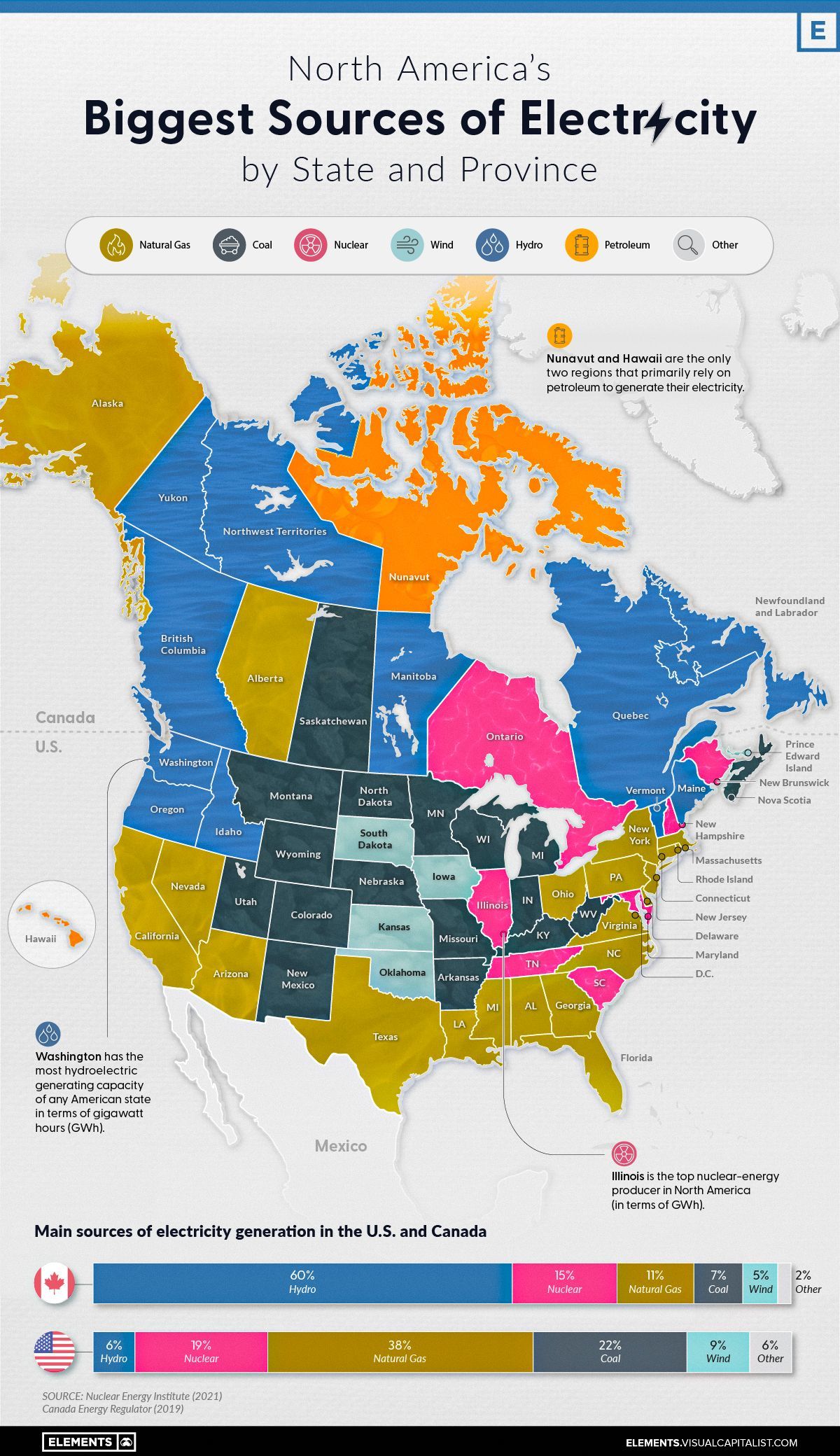
Mapped: Biggest Sources of Electricity by State and Province
On a national scale, the United States and Canada rely on a very different makeup of sources to generate their electricity.
The U.S. primarily uses natural gas, coal, and nuclear power, while Canada relies on both hydro and nuclear. That said, when zooming in on the province or state level, individual primary electricity sources can differ greatly.
Here’s a look at the electricity generation in the states and provinces of these two countries using data from the Nuclear Energy Institute (2021) and the Canada Energy Regulator (2019).
Natural Gas
Natural gas is widely used for electricity generation in the United States. Known as a “cleaner” fossil fuel, its abundance, coupled with an established national distribution network and relatively low cost, makes it the leading electricity source in the country.
In 2021, 38% of the 4120 terawatt-hours (TWh) of electricity generated in the U.S. came from natural gas. Not surprisingly, more than 40% of American states have natural gas as their biggest electricity source.
Here are some states that have the largest shares of natural gas-sourced electricity.
| State/Province | % of Electricity from Natural Gas | Mineral Production Value (2022) |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 Rhode Island | 90.9 | $10.1B |
| 🇺🇸 Delaware | 85.8 | $8.9B |
| 🇺🇸 Massachusetts | 76.9 | $8.0B |
| 🇺🇸 Florida | 73.9 | $5.6B |
| 🇺🇸 Mississippi | 72.1 | $4.8B |
In Canada, natural gas is only the third-biggest electricity source (behind hydro and nuclear), accounting for 11% of the 632 TWh of electricity produced in 2019. Alberta is the only province with natural gas as its main source of electricity.
Nuclear
Nuclear power is a carbon-free energy source that makes up a considerable share of the energy generated in both the U.S. and Canada.
19% of America’s and 15% of Canada’s electricity comes from nuclear power. While the percentages are close to one another, it’s good to note that the United States generates 6 to 7 times more electricity than Canada each year, yielding a lot more nuclear power than Canada in terms of gigawatt hours (GWh) per year.
As seen in the map, many states and provinces with nuclear as their main source of electricity are concentrated in the eastern half of the two countries.
In the U.S., Illinois, Pennsylvania, and South Carolina are top producers in terms of GWh/year. Illinois and South Carolina also have nuclear as their primary electricity source, whereas Pennsylvania’s electricity production from natural gas exceeds that from nuclear.
The vast majority of Canada’s nuclear reactors (18 of 19) are in Ontario, with the 19th in New Brunswick. Both of these provinces rely on nuclear as their biggest source of electricity.
Renewables: Hydro, Wind and Solar
Out of the different types of renewable electricity sources, hydro is the most prevalent in North America. For example, 60% of Canada’s and 6% of the U.S.’s electricity comes from hydropower.
Here are the states and provinces that have hydro as their biggest source of electricity.
| State/Province | % of Electricity from Hydro |
|---|---|
| 🇨🇦 Manitoba | 97 |
| 🇨🇦 Newfoundland and Labrador | 95 |
| 🇨🇦 Quebec | 94 |
| 🇨🇦 British Columbia | 87 |
| 🇨🇦 Yukon | 80 |
| 🇺🇸 Washington | 65 |
| 🇺🇸 Idaho | 51 |
| 🇺🇸 Vermont | 50 |
| 🇨🇦 Northwest Territories | 47 |
| 🇺🇸 Oregon | 46 |
Wind and solar power collectively comprise a small percentage of total electricity generated in both countries. While no state or province relies on solar as its biggest source of electricity, Iowa, Kansas, Oklahoma, and South Dakota rely primarily on wind for their electricity, along with Canada’s Prince Edward Island (PEI).
Coal and Oil
Coal and oil are emission-heavy electricity sources still prevalent in North America.
Currently, 22% of America’s and 7% of Canada’s electricity comes from coal, with places such as Kentucky, Missouri, West Virginia, Saskatchewan, and Nova Scotia still relying on coal as their biggest sources of electricity.
Certain regions also use petroleum to generate their electricity. Although its use for this purpose is declining, it is still the biggest source of electricity in both Hawaii and Nunavut.
Over the next few years, it will be interesting to observe the use of these fossil fuels for electricity generation in the U.S. and Canada. Despite the differences in climate commitments between the two countries, lowering coal and oil-related emissions may be a critical part of hitting decarbonization targets in a timely manner.
Copyright © 2023 Visual Capitalist


Contact
info@vvcresources.com
2369 Kingston Road, PO Box 28059 Terry Town, Scarborough, ON M1N 4E7 Canada
About
Projects
Sign up to receive updates on VVC announcements, launches, and opportunities.
Contact Us
Thank you for signing up!
You will receive VVC updates straight to your inbox.
Please try again later.





